Book a Dermal Filler Consultation at It’s Me and You Clinic with Dr. Laura Geige
Botox is a popular cosmetic treatment that has been widely used to relax facial muscles and reduce wrinkles, but it also has some potential benefits for skin tightening and toning. While Botox is not a substitute for surgical facelifts or other medical treatments, it can be an effective way to improve the appearance of the skin in certain areas.
The mechanism by which Botox tightens and tones the skin involves the inhibition of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates muscle contractions. When Botox is injected into a muscle, it blocks the release of acetylcholine, leading to a relaxation of the muscle and a reduction in muscle activity. This can cause the surrounding tissue to tighten and firm up.
One of the primary ways in which Botox can firm and tone the skin is by reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. By relaxing facial muscles, such as those used for frowning or squinting, Botox can help to decrease the depth and visibility of these wrinkles. This can give the skin a smoother, more youthful appearance.
Botox can also be used to tighten skin on the neck, chin, and jawline, areas that are prone to sagging and laxity as we age. By reducing muscle activity in these areas, Botox can help to restore a more defined jawline and improve the overall contour of the face.
Another benefit of Botox for skin tightening is its ability to reduce pores and improve skin texture. By relaxing facial muscles that pull on the skin, such as those used for raising the eyebrows or forehead, Botox can help to decrease pore size and improve the overall smoothness of the skin.
However, it’s essential to note that Botox is not a replacement for sun protection and skincare routines. To achieve optimal results from Botox treatments, patients must still follow a consistent skincare routine and protect their skin from the sun using broad-spectrum sunscreen and protective clothing.
Additionally, while Botox can provide some tightening effects, it may not be suitable for everyone. Patients with certain medical conditions, such as muscle weakness or paralysis, should avoid Botox treatments. Additionally, individuals with active infections, autoimmune disorders, or recent surgical scars should also exercise caution when considering Botox injections.
For those who do qualify for Botox treatments, the procedure itself is typically straightforward and relatively quick. A trained healthcare professional will administer a series of injections into specific areas of the face or neck, using a sterile needle to minimize discomfort.
The results of Botox treatments can last anywhere from several months to over two years, depending on individual factors such as muscle activity, lifestyle, and genetics. To maintain optimal results, patients typically require repeat treatments every 3-6 months.
In summary, while Botox is not a substitute for surgical facelifts or other medical treatments, it can be an effective way to firm, tone, and tighten the skin in specific areas. By understanding its benefits and limitations, patients can make informed decisions about whether Botox is right for them.
How Does Botox Work for Skin Tightening?
Botox, a neurotoxin protein, has gained popularity over the years due to its ability to temporarily relax facial muscles, reducing wrinkles and fine lines. However, its mechanism of action extends beyond just cosmetic applications, allowing it to contribute to skin tightening as well.
- Botox works by blocking the release of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine, which signals muscle contractions.
- When Botox is injected into a muscle, it prevents the acetylcholine receptors from binding with the neurotransmitter, thereby inhibiting muscle contraction.
- This inhibition leads to a decrease in muscle activity, causing the skin above the muscle to relax and contract less, resulting in a more youthful appearance.
The process of Botox-induced skin tightening is multifaceted, involving both the relaxation of facial muscles and the enhancement of collagen production. When facial muscles are constantly contracted, they can lead to a breakdown in the skin’s structural integrity.
Collagen, an essential protein for skin elasticity, can become depleted over time due to repeated muscle contractions. Botox helps to reverse this process by reducing muscle activity, allowing the skin to recover and replenish its collagen stores.
- Increased collagen synthesis: By reducing muscle contraction and allowing the skin to relax, Botox stimulates the production of new collagen fibers, leading to improved skin elasticity and firmness.
- Improved skin texture: As collagen production increases, so does the skin’s ability to maintain its structural integrity, resulting in a smoother, more even-toned complexion.
- Reduced sagging: With the reduction of muscle activity, the skin above the treated area is able to regain its natural shape and firmness, reducing the appearance of sagging and jowls.
In addition to collagen production, Botox has also been shown to stimulate the growth of new blood vessels in the treated areas. This increased blood flow brings more oxygen and nutrients to the skin, further contributing to its tightening effect.
Furthermore, Botox can help improve skin firmness by increasing the activity of fibroblasts, cells responsible for producing elastin and collagen. Elevated elastin levels lead to improved skin elasticity and reduced wrinkles.
While Botox is often associated with cosmetic applications, its mechanism of action has significant implications for the treatment of various conditions, such as excessive sweating, migraines, and muscle spasms. Its ability to induce skin tightening makes it an attractive option for those seeking a more comprehensive approach to anti-aging.
Botox, a neurotoxin protein derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, has been widely used to relax facial muscles and reduce wrinkles. However, recent research suggests that it may also have benefits for skin tightening.
When Botox is injected into the skin, it temporarily blocks the release of a chemical signal called acetylcholine, which stimulates muscle contraction. As a result, the muscle becomes relaxed and no longer contracts, leading to reduced wrinkles and fine lines.
But how does this translate to skin tightening? The answer lies in the way Botox affects the underlying structure of the skin. When skin loses its elasticity due to aging or other factors, it can sag and lose its firmness. By relaxing the underlying muscles that contract and tighten the skin, Botox can help restore some of this lost elasticity.
For example, when we age, our facial skin is subject to repeated contractions and relaxations as we express emotions like frowning or smiling. These micro-contracts can lead to the formation of fine lines and wrinkles, which are caused by the loss of collagen and elastin fibers in the dermal layer of the skin.
Botox can help mitigate this process by relaxing the muscles that cause these contractions. By reducing the number of times a muscle contracts, Botox can help prevent the breakdown of collagen and elastin fibers, which are essential for maintaining skin elasticity.
In addition to its effects on facial wrinkles, research suggests that Botox may also have benefits for other areas of the body, such as the abdomen and arms. By relaxing muscles in these areas, Botox can help reduce the appearance of sagging skin and improve overall contours.
Schedule a Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige
While the scientific evidence is still emerging, studies have shown that Botox can lead to significant improvements in skin elasticity and firmness. For example, one study published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology found that Botox injections resulted in a 34% improvement in skin elasticity after just six months.
Another benefit of using Botox for skin tightening is that it can be used in conjunction with other cosmetic treatments, such as fillers and laser therapy. By combining these treatments, patients may experience even more dramatic improvements in skin texture and appearance.
However, it’s essential to note that Botox is not a substitute for traditional skin tightening treatments like facelifts or chemical peels. While Botox can help improve the appearance of sagging skin, it may not address deeper structural issues that require more invasive procedures.
To get the most out of Botox for skin tightening, patients should work with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment. This may involve a series of injections spaced several months apart, depending on individual results and patient preferences.
Overall, the use of Botox for skin tightening is a promising area of research that shows great promise for improving skin elasticity and firmness. While more studies are needed to fully understand its benefits and limitations, patients may find it a valuable addition to their cosmetic treatment arsenal.
Botox, a neurotoxin protein derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, has been widely used in cosmetic procedures to temporarily relax facial muscles and reduce wrinkles. However, its effects on skin tightening are more complex and have garnered significant scientific attention in recent years.
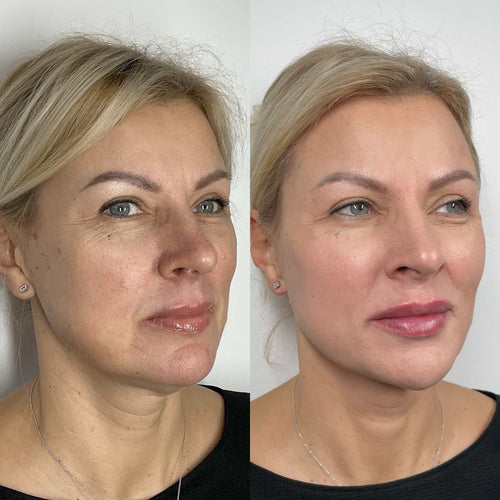

When administered into the skin, Botox works by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that signals muscle contractions. In the context of skin tightening, Botox is typically injected into specific areas of concern, such as the nasolabial folds or marionette lines.
The process of skin tightening via Botox involves the contraction of surrounding muscles, which in turn causes the injection site to sink slightly into the skin. This effect is often referred to as “skin pinching” or “muscle contractions-induced skin shortening.”
Research has shown that repeated injections of Botox can lead to a gradual tightening of the overlying skin, particularly when administered in combination with other treatments such as fillers or chemical peels.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that patients who received regular Botox treatments for facial wrinkles experienced significant improvements in skin elasticity and firmness after six months of treatment.
Another study published in the International Journal of Cosmetic Science demonstrated that Botox injections into the platysma muscle, which runs from the ear to the chin, can lead to increased skin tightness and a more defined jawline over time.
The mechanism behind Botox-induced skin tightening is thought to involve the stimulation of collagen production in the dermal layer of the skin. When Botox blocks acetylcholine receptors, it triggers a cascade of signals that ultimately leads to an increase in fibroblast activity and collagen synthesis.
These effects have been observed in both animal models and human subjects, with studies suggesting that repeated Botox injections can lead to lasting improvements in skin texture and tone over several months or even years.
While the exact mechanisms behind Botox-induced skin tightening are not yet fully understood, research suggests that its effectiveness is multifaceted and involves a combination of muscle contraction, collagen stimulation, and dermal remodeling.
In terms of clinical implications, these findings suggest that Botox may be an effective adjunctive treatment for patients seeking to achieve more radiant and youthful-looking skin through skin tightening and toning.
Botox is a popular cosmetic treatment that has been widely used to relax facial muscles and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. However, its benefits extend beyond just wrinkle reduction, as research has shown that it can also play a role in _skin tightening_. In this response, we will explore how Botox works for skin tightening and examine the scientific evidence behind its effectiveness.
_Botox Mechanism of Action_
Botox, also known as botulinum toxin, is a neurotoxin that works by temporarily paralyzing muscles. When injected into a muscle, it blocks the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that signals the muscle to contract. This results in a temporary “freezing” of the muscle, which can help reduce the appearance of sagging and improve skin elasticity.
_The Role of Facial Muscles in Skin Sagging_
Facial muscles, including the forehead, frown, and crow’s feet, play a significant role in maintaining the youthful appearance of the skin. When these muscles contract, they pull on the overlying skin, causing it to stretch and sag over time. By relaxing these muscles through Botox injections, patients can reduce the amount of stretching and sagging that occurs.
_The UCLA Study_
University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) researchers conducted a study on the effects of Botox on facial sagging and skin elasticity. The results showed that botulinum toxin injections can decrease facial sagging and improve skin elasticity in patients with moderate to severe facial wrinkles.
_The University College London Study_
Similar findings were reported by scientists at University College London, who found that Botox treatment reduced signs of aging after injection. This study suggests that the use of Botox may be a valuable tool in the prevention and treatment of facial sagging.
_Other Factors That Contribute to Skin Tightening_
While Botox can certainly contribute to skin tightening, it is not the only factor at play. Other treatments, such as laser therapy, chemical peels, and dermal fillers, may also be used in conjunction with Botox to achieve optimal results.
_The Combination of Botox and Other Treatments_
Some research has explored the use of a combination of treatments, including Botox, laser therapy, and dermal fillers. This approach may offer improved results by targeting multiple aspects of skin aging, such as wrinkle reduction, skin elasticity, and facial sagging.
_The Future of Botox for Skin Tightening_
As research continues to uncover the benefits of Botox for skin tightening, we can expect to see new and innovative applications for this treatment in the years to come. Whether used alone or as part of a comprehensive treatment plan, Botox has the potential to play a major role in maintaining youthful, radiant-looking skin.
Book Your Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige
Precautions and Side Effects
Botox is a popular non-surgical treatment used for skin tightening, but like any other medical procedure, it carries its own set of precautions, side effects, risks, and complications that patients should be aware of.
Precautions: Before undergoing Botox for skin tightening, patients must ensure they have realistic expectations about the treatment’s outcomes. It is essential to note that Botox is not a substitute for surgery or other medical treatments and may not produce the desired results in everyone. Patients with certain medical conditions, such as blepharospasm, eyelid spasms, or facial asymmetry, should avoid undergoing Botox treatment.
Additionally, patients should inform their doctor about any medications they are taking, including blood thinners, immunosuppressants, and muscle relaxants, as these may interact with the Botox treatment. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also avoid Botox, as its effects on the developing fetus or baby are unknown.
Side Effects: Common side effects of Botox for skin tightening include temporary bruising, swelling, redness, and swelling at the injection site. These side effects are usually mild and resolve on their own within a few days to a week after treatment. More severe side effects, such as droopy eyelids, eyebrow asymmetry, or facial weakness, can occur but are rare.
Risks: The primary risk associated with Botox for skin tightening is the spread of the toxin to surrounding areas, which can cause unwanted effects like eyelid drooping, facial weakness, or difficulty swallowing. This risk is highest during the initial treatment and decreases over time.
Complications: In rare cases, Botox can lead to serious complications, including botulism, a condition that affects the nervous system and can be life-threatening. Botulism symptoms include muscle weakness, respiratory problems, and difficulty swallowing or speaking.
Other potential complications of Botox for skin tightening include eyelid ptosis (drooping) or enophthalmos (sinking of the eyes into the orbit), which can be permanent in some cases. Asymmetry, where one side of the face appears more affected than the other, is another possible complication.
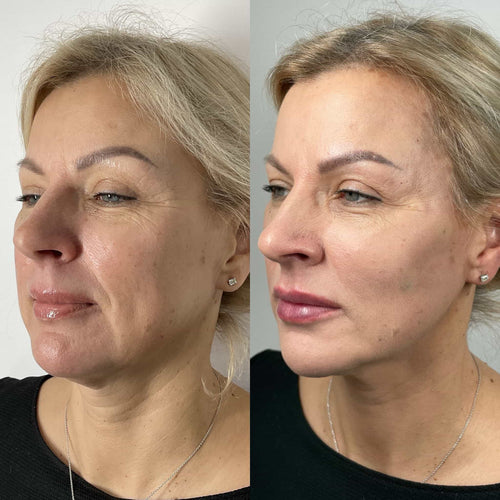
Long-term Risks: While Botox for skin tightening has a relatively low risk of long-term complications, repeated treatments can lead to decreased effectiveness over time. This can result in the need for more frequent or higher doses of Botox, which may increase the risk of side effects and complications.
It is essential for patients to follow their doctor’s post-treatment instructions carefully to minimize the risk of complications and ensure optimal results. Regular follow-up appointments with the doctor are also crucial to monitor the treatment’s effectiveness and address any concerns or issues that arise.
In rare instances, Botox can lead to an allergic reaction or hypersensitivity response, which may cause symptoms like hives, itching, or swelling. If a patient experiences any unusual reactions after Botox treatment, they should seek immediate medical attention.
Botox is a popular cosmetic treatment used to relax facial muscles and reduce wrinkles and fine lines, but like any medical procedure, it carries certain risks and potential side effects.
While generally considered safe, Botox can cause bruising, swelling, and eyelid drooping (ptosis), particularly in individuals over the age of 65.
Ptosis is a condition where the eyelid becomes droopy or heavy, which can be temporary or permanent depending on the severity of the reaction.
Other potential side effects of Botox include redness, itching, and swelling at the injection site, as well as dry eye syndrome.
In rare cases, Botox injections can spread to other areas of the face or body, known as a “diffuse” reaction.
A diffuse reaction occurs when the toxin spreads beyond the intended injection site, causing symptoms in multiple locations on the body.
This rare but serious complication requires immediate medical attention and may require additional treatment to alleviate symptoms.
Diffuse reactions can occur due to various factors, including improper technique by the healthcare provider, using expired or low-quality Botox products, or pre-existing conditions such as neuromuscular disorders.
Additionally, certain medications, such as blood thinners and immunosuppressants, can increase the risk of complications during Botox treatment.
Individuals with a history of eye problems, nerve damage, or muscle weakness should consult their doctor before undergoing Botox treatment to discuss potential risks and side effects.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also exercise caution when considering Botox treatment due to the limited data available on its safety in these populations.
Overall, while Botox is generally considered safe, it’s essential for individuals to carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks and discuss their individual situation with a qualified healthcare provider before undergoing treatment.
Botox is a popular cosmetic treatment used to temporarily relax facial muscles, but it’s not a substitute for surgical skin tightening procedures. Before considering Botox for skin tightening, it’s essential to understand the precautions and potential side effects involved.
Precautions to consider before trying Botox for skin tightening include: having realistic expectations about the results, as Botox is not a substitute for exercise, weight loss, or sun protection. Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as droopy eyelids (ptosis), facial paralysis, or muscle weakness, should avoid Botox treatment.
Other precautions to be aware of include: taking certain medications, such as blood thinners or painkillers, which may interact with Botox. Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should consult their doctor before undergoing Botox treatment. People with a history of neuromuscular disorders, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) or myasthenia gravis, should exercise caution when considering Botox.
Common side effects of Botox include: bruising, swelling, redness, and pain at the injection site. In rare cases, more severe reactions may occur, such as eye drooping, eyebrow asymmetry, or difficulty swallowing (dysphagia). These reactions are usually temporary and resolve on their own within a few weeks.
More serious side effects can include: spread of the toxin to other areas of the body, which can cause symptoms like numbness, weakness, or paralysis. In rare cases, Botox has been linked to systemic complications, such as cardiac problems or respiratory failure.
Alternatives to consider before trying Botox for skin tightening include: non-surgical skin tightening procedures like radiofrequency treatments, microneedling, or chemical peels. These alternatives can be less invasive and may offer more long-lasting results without the risks associated with Botox.
For individuals seeking more dramatic results, surgical skin tightening procedures like facelifts or body contouring surgeries may be a better option. However, these procedures carry their own set of risks and complications, and should only be considered after consulting with a qualified medical professional.
No non-invasive skin tightening treatments are completely devoid of risks, and potential side effects can range from mild to severe.
Individuals seeking noninvasive skin tightening treatments should be aware that these methods may not offer the same level of longlasting results as more invasive procedures like facelifts, laser resurfacing, and chemical peels.
The Mayo Clinic suggests that these alternative methods can provide more durable outcomes compared to Botox injections, which typically last for 36 months.
However, noninvasive skin tightening treatments still carry some risks, including swelling, bruising, redness, and inflammation at the treatment site.
In rare cases, adverse reactions such as allergic responses or anaphylaxis can occur.
Additionally, some individuals may experience temporary numbness or tingling sensations in the treated area, which usually resolves on its own within a few days.
Facial asymmetry, also known as facial unevenness or asymmetry of the face, is another potential side effect of noninvasive skin tightening treatments.
This condition can cause one side of the face to appear more defined or lifted compared to the other, resulting in an uneven appearance that may not be desirable for some individuals.
It is also possible for temporary changes in skin texture and tone to occur, such as hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation, which can result in dark spots or discoloration of the treated area.
In rare instances, noninvasive skin tightening treatments may lead to more severe complications, including nerve damage, eyelid drooping, or facial weakness.
Individuals seeking noninvasive skin tightening treatments should carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks associated with these methods and consider alternative procedures like facelifts, laser resurfacing, and chemical peels that may offer more longlasting results.
Read more about Derwen Roots here. Read more about On the Carpet here. Read more about Gifted Brits here. Read more about Josie Barrett here.
- Why Breadcrumbing Is One Of The Most Subtle Forms Of Manipulation In Relationships - November 11, 2025
- What Is The Average Age For Cheek Fillers? - November 10, 2025
- What Age Is Too Late For A Facelift? - November 7, 2025
