Introduction:
- Explanation of cannabinoids as chemical compounds found in cannabis plants.
- Overview of the growing interest in cannabinoids for their potential therapeutic properties.
- Introduction to the purpose and structure of the guide.
Understanding Cannabinoids:
1.1 Definition and Properties
- Definition of cannabinoids as naturally occurring compounds specific to the cannabis plant.
- Explanation of their interaction with the body’s endocannabinoid system and their potential effects on various physiological processes.
1.2 Types of Cannabinoids
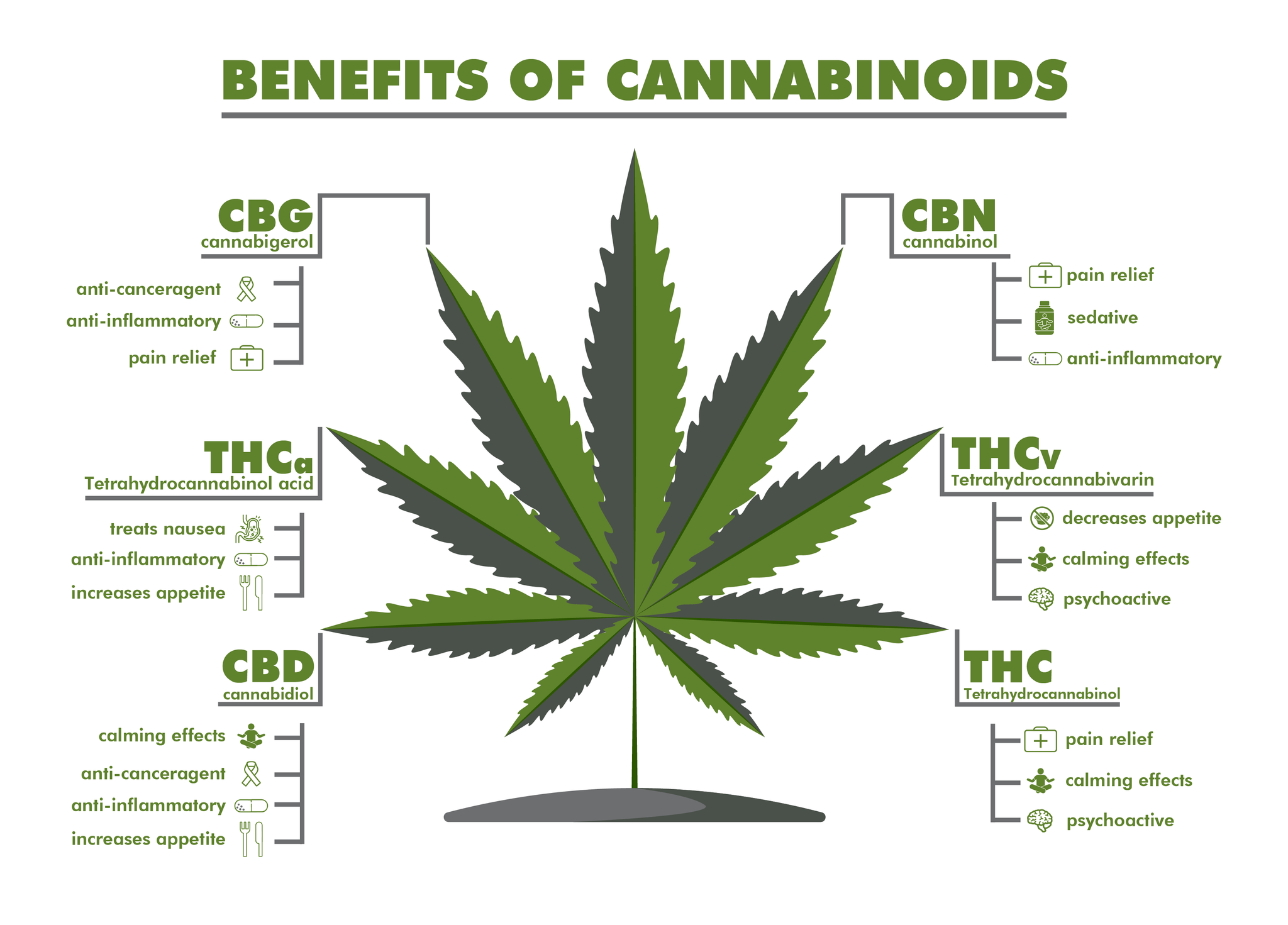
- Introduction to the different categories of cannabinoids, including phytocannabinoids, endocannabinoids, and synthetic cannabinoids.
- Overview of their sources and the variations in their effects.
Major Phytocannabinoids:
2.1 Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
- Detailed description of THC as the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis.
- Explanation of its effects on the body, including its potential for euphoria, relaxation, and pain relief.
2.2 Cannabidiol (CBD)
- In-depth exploration of CBD as a non-intoxicating cannabinoid with various potential therapeutic benefits.
- Discussion of its effects on anxiety, inflammation, pain, and other health conditions.
2.3 Cannabigerol (CBG)
- Overview of CBG as a precursor cannabinoid and its potential as an anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and neuroprotective agent.
- Explanation of its role in the biosynthesis of other cannabinoids.
2.4 Cannabinol (CBN)
- Description of CBN as a degradation product of THC with potential sedative and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Discussion of its potential use in promoting sleep and alleviating pain.
2.5 Other Phytocannabinoids
- Brief overview of minor cannabinoids, such as cannabichromene (CBC), cannabidivarin (CBDV), and tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV).
- Explanation of their potential effects and ongoing research on their therapeutic applications.
Lesser-Known Cannabinoids:
3.1 Cannabichromenic Acid (CBCA)
- Description of CBCA as the precursor to CBC and its potential anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties.
- Discussion of its potential therapeutic applications.
3.2 Cannabidivarinic Acid (CBDVA)
- Overview of CBDVA as a precursor to CBDV and its potential antiepileptic and anti-nausea effects.
- Explanation of its ongoing research and potential therapeutic uses.
3.3 Tetrahydrocannabivarin Acid (THCVA)
- Description of THCVA as the precursor to THCV and its potential antiepileptic, anti-inflammatory, and appetite-suppressing properties.
- Discussion of its potential therapeutic applications.
Synthetic Cannabinoids:
4.1 Definition and Use
- Explanation of synthetic cannabinoids as laboratory-created compounds that mimic the effects of natural cannabinoids.
- Discussion of their use in research, medicine, and recreational purposes.
4.2 Examples and Concerns
- Overview of specific synthetic cannabinoids, such as JWH-018 and Spice, and their association with adverse health effects and legal concerns.
- Explanation of the risks associated with unregulated synthetic cannabinoids.
The Entourage Effect:
- Introduction to the concept of the entourage effect, which suggests that cannabinoids and other compounds in cannabis work synergistically to produce enhanced effects.
- Discussion of the potential benefits of consuming whole-plant cannabis products containing multiple cannabinoids
and how they may offer a more comprehensive therapeutic experience compared to isolated cannabinoids.
Potential Therapeutic Applications:
6.1 Pain Management
- Explanation of how cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD, may help alleviate various types of pain, including chronic pain, neuropathic pain, and inflammatory pain.
- Discussion of the mechanisms of action and supporting scientific studies.
6.2 Anxiety and Depression
- Overview of the potential anxiolytic and antidepressant properties of cannabinoids, particularly CBD.
- Examination of relevant research studies and anecdotal evidence supporting their use in managing anxiety and depression symptoms.
6.3 Neurological Disorders
- Exploration of the potential benefits of cannabinoids in neurological conditions, such as epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson’s disease.
- Discussion of the impact of cannabinoids on neuroprotection, neuroinflammation, and symptom management.
6.4 Cancer Support
- Overview of the potential anti-tumor properties of cannabinoids, including their role in inhibiting tumor growth and promoting apoptosis.
- Examination of ongoing research and its implications for cancer treatment and symptom management.
6.5 Sleep Disorders
- Discussion of how cannabinoids, particularly CBD, may help regulate sleep patterns and improve sleep quality.
- Exploration of relevant studies and potential mechanisms of action.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions:
- Explanation of potential side effects associated with cannabinoids, such as dry mouth, dizziness, and changes in appetite.
- Discussion of drug interactions and precautions, particularly for individuals taking medications or with underlying health conditions.
- Emphasis on the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional before using cannabinoids for therapeutic purposes.
Legal Considerations:
- Overview of the legal status of cannabinoids, including variations in laws and regulations across different jurisdictions.
- Explanation of the distinction between hemp-derived CBD and marijuana-derived CBD in terms of legality and THC content.
- Discussion of the importance of sourcing CBD products from reputable and compliant sources.
Conclusion
- Recap of the different cannabinoids found in cannabis and their potential therapeutic benefits.
- Encouragement for individuals to explore further research, consult with healthcare professionals, and consider individual needs and preferences when considering cannabinoids for therapeutic use.
- Final thoughts on the evolving landscape of cannabinoid research and its potential to contribute to the development of novel treatments and therapies.
Note: The comprehensive guide on cannabinoids can be further expanded by providing more in-depth information on additional cannabinoids, including their specific effects, ongoing research, and potential therapeutic applications. The inclusion of scientific references, case studies, and personal anecdotes can enhance the credibility and practicality of the guide.
- Best Delta 10 THC Disposables Reviewed - November 8, 2023
- Comprehensive Guide on the Benefits of Agrimony Supplements - November 8, 2023
- Comprehensive Guide on the Benefits of Lion’s Mane Functional Mushrooms - November 8, 2023